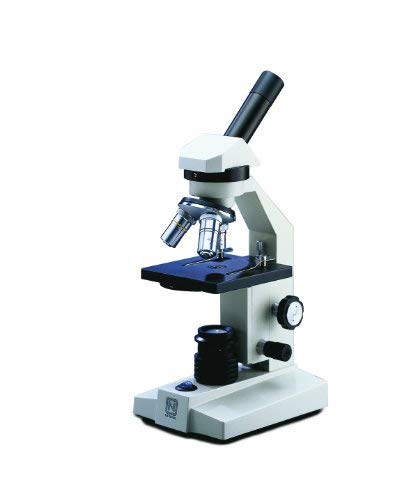
The National Optical 205-RLED Basic Monocular Compound Microscope has a 10x widefield eyepiece with pointer, a reverse-mounted nosepiece with three objectives, LED illumination, separate coarse and fine focus, a disc diaphragm, and a plain stage with stage clips. The monocular viewing head has a fixed inclination to reduce eye and neck strain, and 360-degree rotation capability to enable sharing. An eyepiece pointer is used to identify features for students. A reverse-mounted nosepiece keeps objectives out of the way to prevent damage and contamination, and to enable more secure slide handling. Rotation positions with secure, positive stops ensure accurate positioning and support a range of magnification options. The 40xR objective is retractable and spring-loaded to prevent damage to the slide or objective when focusing. A basic compound microscope is used in classroom, home school, and hobbyist settings for inspection and dissection of specimens when two-dimensional images are desired.
The microscope has lower (diascopic) Brightfield illumination that transmits light up through the specimen for enhanced visibility of translucent and transparent objects. Brightfield (BF) illumination allows the specimen to absorb light, resulting in a dark image on a light background. The LED light source provides bright, cool light for working with temperature-sensitive or live specimens, and operates on rechargeable batteries for cordless operation. A rheostat controls the amount of light emanating from the lamp. A disc diaphragm controls the amount of light illuminating the specimen. The plain stage has an opening for light transmission, and stage clips to secure the slide or specimen in place while viewing. Separate coarse and fine focus knobs speed focusing. A stage stop prevents the stage or specimen from coming into contact with the objectives, and a focus tension control prevents stage drift. The cast aluminum frame provides durability and has a gray enamel finish.
| Microscope Head and Optics Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Head | Monocular |
| Magnification range | 40x-400x |
| Head inclination | 45 degrees |
| Eyepiece (18mm) | WF10x |
| Nosepiece | Reverse-mounted |
| Objectives | 4x, 10x, 40xR (retractable) |
| Microscope Illumination and Stage Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Focus type | Separate coarse and fine |
| Light source | LED |
| Diaphragm | Disc |
| Illumination type | Brightfield |
| Stage type | Plain |
| Stage dimensions | 110 x 120mm (W x D) |
| Power | (3) rechargeable AA nickel metal hydride (NiMH) batteries |
W is width, the horizontal distance from left to right; D is depth, the horizontal distance from front to back.
Microscopes are instruments used to enhance the resolution of an object or image. Types include compound, stereo, or digital. Compound microscopes use a compound optical system with an objective lens and an eyepiece. Stereo microscopes show object depth in a three-dimensional image. Digital microscopes are used to display an image on a monitor, rather than looking through a lens. Microscopes can have monocular (one), binocular (two), or trinocular (three) eyepieces, with varying magnification abilities. Magnification ability refers to the size of an image. Resolution, also known as resolvant power, refers to the clarity of the image. The interaction between field of view (FOV), numerical aperture (NA), and working distance (WD) determines resolution. Microscopes can control magnification through a fixed focus, or through a range of adjustments. They can also utilize LED, fluorescent, and mirror light sources to help control viewing capabilities. Microscopes are widely used in education, lab research, biology, metallurgy, engineering, chemistry, manufacturing, and in the medical, forensic science, and veterinary industries.
National Optical and Scientific Instruments manufactures microscopes and microscope cameras. The company, founded in 1991, is headquartered in Schertz, TX.
What’s in the Box?
- National Optical 205-RLED Basic Monocular Compound Microscope
- WF10x eyepiece, 18mm
- 4x objective
- 10x objective
- 40xR (retractable) objective
- (3) rechargeable NiMH AA batteries
- Battery charger
- Hex key wrench
- Dust cover
- Instructions